Winches are essential tools for off-road enthusiasts, commercial operators, and anyone needing to pull heavy loads. One of the critical aspects to consider when choosing a winch is its voltage.
This guide will help you understand the differences between 12V and 24V winches, their pros and cons, and how to select the best option for your needs.
Quick summary
When comparing 12V and 24V winches, 12V winches are easier and cheaper to install, suitable for light to moderate use, while 24V winches offer higher power, faster line speeds, and greater efficiency, ideal for heavy-duty and frequent use.
Understanding Voltage in Winches
Voltage in winch systems is the electrical potential powering the winch motor. Higher voltage allows the motor to draw more power from the vehicle’s battery.
How Voltage Affects Winch Performance
- Power Output: Higher voltage enables the winch to produce more power, essential for heavy loads.
- Current Draw: Higher voltage reduces the current needed for a given power output, easing the load on the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Efficiency: Higher voltage systems are more efficient, converting more electrical energy into mechanical energy with less heat loss.
12V Winches: Pros and Cons

Advantages of 12V Winches
Compatibility with Most Vehicles:
- Explanation: The majority of vehicles, especially passenger cars, trucks, and SUVs, are equipped with a 12V electrical system. This makes 12V winches compatible with a wide range of vehicles without requiring any additional modifications or equipment.
- Benefit: This widespread compatibility means you can easily install a 12V winch on most vehicles without worrying about electrical system incompatibility. It simplifies the process for most users, particularly those who do not want to make extensive changes to their vehicle’s setup.
Lower Cost:
12V winches are generally more affordable than 24V winches. The cost difference arises because 12V systems are more common and their components are produced in larger quantities, reducing manufacturing costs.
Benefit: For users on a budget or those who need a winch for occasional use, the lower cost of 12V winches makes them an attractive option. It allows more people to have access to winching capabilities without a significant financial investment.
Simpler Installation:
Installing a 12V winch is usually straightforward. Since it matches the standard vehicle electrical system, it often involves connecting a few wires and mounting the winch, without needing extensive modifications.
Benefit: The simpler installation process saves time and effort. It is particularly beneficial for DIY enthusiasts who prefer to install the winch themselves rather than paying for professional installation services.
Disadvantages of 12V Winches
Lower Power Output:
12V winches generally provide less power compared to their 24V counterparts. This is because the power output is limited by the voltage, which can affect the winch’s ability to handle heavy loads efficiently.
Drawback: For heavy-duty applications, such as pulling large vehicles or working in demanding environments, the lower power output of a 12V winch may be insufficient. Users may find that the winch struggles with heavier tasks, limiting its usefulness.
Slower Line Speed:
The line speed of a winch refers to how quickly the cable can be wound in or out. 12V winches typically have slower line speeds due to their lower power output and higher current draw.
Drawback: In situations where speed is critical, such as vehicle recovery in dangerous conditions, a slower line speed can be a significant disadvantage. It can prolong recovery time and increase the risk of further complications.
Higher Amperage Draw:
A 12V winch draws more current (amperage) to produce the same power output as a higher voltage winch. This higher amperage draw can strain the vehicle’s battery and electrical system, potentially leading to quicker battery depletion and overheating.
Drawback: The increased strain on the vehicle’s electrical system can result in more frequent battery recharges and the need for a more robust electrical setup.
This can be inconvenient and may necessitate additional investments in battery and electrical system upgrades to ensure reliable winch operation.
24V Winches: Pros and Cons

Advantages of 24V Winches
Higher Power Output:
A 24V winch can generate more power compared to a 12V winch because it operates at a higher voltage. Power output is directly related to voltage, so doubling the voltage generally allows the winch to produce significantly more power without needing to increase the current.
Benefit: This increased power output makes 24V winches ideal for handling heavier loads and more demanding winching tasks. For instance, in situations where you need to recover a large vehicle or pull heavy equipment, the higher power output ensures the winch can perform these tasks more efficiently and effectively.
Faster Line Speed:
Line speed refers to the speed at which the winch cable is wound in or out. Higher voltage winches, like those operating at 24V, typically have a faster line speed because the motor can operate more efficiently at higher voltages.
Benefit: Faster line speeds are crucial in critical recovery situations where time is of the essence.
For example, if a vehicle is stuck in a precarious position, a winch with a faster line speed can pull it out more quickly, reducing the time spent in a dangerous situation and improving overall safety.
Lower Amperage Draw:
Amperage (current) draw is inversely related to voltage when producing a given amount of power.
A 24V winch requires less current to produce the same power output as a 12V winch. This means the electrical system experiences less strain with a 24V winch.
Benefit: The lower amperage draw reduces the load on the vehicle’s battery and electrical components, which can enhance their longevity and reliability.
It also means the electrical system is less likely to overheat or suffer from excessive wear, making the winch and the vehicle’s electrical system more reliable in the long term.
Disadvantages of 24V Winches
Limited Vehicle Compatibility:
Most vehicles, especially standard passenger vehicles, operate on a 12V electrical system. To use a 24V winch, you need a vehicle that either already operates on 24V (which is rare) or you need to modify the vehicle to support a 24V system.
Drawback: This limited compatibility means that many users will need to invest in additional equipment, such as a second battery and wiring to set up a 24V system. These modifications can be time-consuming and costly, and they might not be feasible for all vehicles.
Higher Cost:
- Explanation: 24V winches and the necessary components to modify a vehicle’s electrical system to support 24V are typically more expensive than 12V winches. This includes the winch itself, the additional battery, and any other necessary electrical components.
- Drawback: The higher cost can be a significant barrier for many users, especially those on a budget or those who do not require the additional power and speed offered by a 24V winch. The initial investment and potential ongoing costs for maintenance and battery replacements need to be considered.
More Complex Installation:
Installing a 24V winch usually involves more complex wiring and setup compared to a 12V winch. This often requires a dual battery system, which involves additional wiring, battery mounts, and possibly upgrading other electrical components to handle the increased voltage.
Drawback: The complexity of the installation can deter some users, especially those without technical expertise or those who do not want to spend money on professional installation services. It increases the time and effort required to set up the winch and can introduce more points of potential failure if not done correctly.
Comparing Performance of 12V and 24V Winches
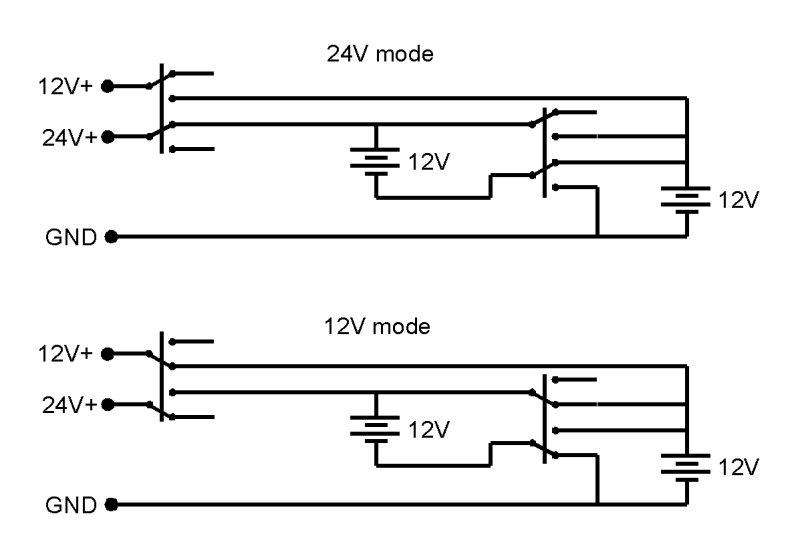
Power Output Comparison
24V Winches:
4V winches can generate more power than 12V winches. This is because power output (measured in watts) is a product of voltage and current (P = V x I). With a higher voltage, the winch can produce more power without needing a proportional increase in current.
Benefit: This higher power output makes 24V winches more suitable for heavy-duty tasks such as pulling larger vehicles or heavy loads.
They can handle more demanding applications effectively, making them ideal for commercial and industrial use where higher power is often necessary.
12V Winches:
12V winches have lower power output because they operate at a lower voltage. To achieve the same power output as a 24V winch, a 12V winch would need to draw twice the current, which is not always feasible due to limitations in the vehicle’s electrical system.
Drawback: The lower power output of 12V winches can limit their effectiveness in heavy-duty scenarios. They are more suitable for lighter loads and occasional use where the demands are not as high.
Line Speed Comparison
24V Winches:
Line speed refers to how quickly the winch cable can be wound in or out. 24V winches generally have faster line speeds because the higher voltage allows the motor to operate more efficiently and at higher speeds.
Benefit: Faster line speeds are particularly advantageous in emergency recovery situations where time is critical.
For example, when a vehicle is stuck in a precarious position, a faster line speed can expedite the recovery process, reducing the time spent in a potentially dangerous situation.
12V Winches:
12V winches tend to have slower line speeds due to their lower voltage and power output. The motor operates at a slower pace, resulting in a slower movement of the winch cable.
Drawback: The slower line speed of 12V winches can be a disadvantage in situations where speed is essential. It can prolong recovery times and potentially increase the risk in emergency scenarios.
Efficiency and Heat Generation
24V Winches:
Efficiency in winches is measured by how well the electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy with minimal losses.
24V systems are generally more efficient because they operate at a higher voltage, reducing the current required for the same power output. Lower current means less energy is lost as heat.
Benefit: The increased efficiency of 24V winches results in less heat generation during operation. This reduction in heat enhances the longevity of the winch components, as excessive heat can lead to faster wear and tear and potential failure of parts.
12V Winches:
12V winches are less efficient because they draw more current to achieve the same power output as a 24V winch. The higher current leads to greater energy losses in the form of heat.
Drawback: The lower efficiency and higher heat generation can shorten the lifespan of the winch components.
Frequent or prolonged use can lead to overheating issues, which may require more frequent maintenance and potentially shorten the overall lifespan of the winch.
D. Battery Drain and Recovery Time
24V Winches:
Because 24V winches draw less current for the same power output, they put less strain on the vehicle’s battery. This reduced current draw means the battery can supply power for longer periods without depleting as quickly.
Benefit: The lower strain on the battery leads to quicker recovery times and reduces the risk of battery drain.
This is particularly beneficial for users who need to use the winch frequently or for extended periods, as it ensures the battery remains in good condition and is less likely to fail during critical operations.
12V Winches:
12V winches require more current to produce the same power as a 24V winch, leading to a higher strain on the vehicle’s battery. This increased demand can cause the battery to deplete more quickly and take longer to recover.
Drawback: The higher battery drain and longer recovery times can be problematic for users who need reliable and sustained winch operation.
Frequent or prolonged use can lead to battery failures, requiring more frequent recharges or replacements and potentially leaving the winch unusable when needed most.
Choosing the Right Winch for Your Vehicle
A. Assessing Your Vehicle’s Electrical System
Understanding Your Vehicle’s Capacity:
Before selecting a winch, it’s crucial to understand your vehicle’s electrical system capacity. Most vehicles operate on a 12V electrical system, but some heavy-duty vehicles and military or commercial vehicles may use a 24V system.
Modifications Required: If your vehicle operates on a 12V system and you want to install a 24V winch, you’ll need to make significant modifications.
This might include installing a dual battery setup, changing the alternator, and rewiring parts of the vehicle to handle the higher voltage.
Checking Compatibility: Verify that the alternator, battery, and wiring in your vehicle can handle the current draw of the winch.
For example, a high-current draw from a powerful 12V winch can overstrain an older or weaker electrical system, potentially causing failures.
B. Considering Your Typical Winching Needs
Evaluating Load and Usage Scenarios:
Consider the typical scenarios in which you will use the winch. This includes the types of loads you will be pulling, the frequency of use, and the environment in which the winch will operate.
Power and Speed Requirements: For light, occasional use, such as pulling a small vehicle or recovering a stuck ATV, a 12V winch may suffice.
However, for heavy-duty tasks, such as recovering large trucks or frequent use in commercial settings, a 24V winch’s higher power output and faster line speed may be necessary.
Environmental Factors: Think about the conditions you’ll be working in. Harsh environments with mud, water, or extreme temperatures may require a winch with greater durability and power to handle the increased resistance and challenging conditions.
C. Evaluating Your Budget
Cost Analysis:
The cost of the winch itself is just one part of the total expense. You must also consider the cost of any necessary modifications and additional components, such as extra batteries, upgraded alternators, or specialized mounting hardware.
12V Winch Costs: Typically, 12V winches are more affordable and don’t require extensive modifications, making them a cost-effective option for many users.
24V Winch Costs: Although 24V winches offer better performance, they are generally more expensive. The installation of a 24V system can significantly increase the overall cost due to the need for additional electrical components and professional installation services if you’re not comfortable doing it yourself.
Long-term Considerations: Consider the long-term costs, including maintenance and potential replacements.
A higher initial investment in a 24V winch may save money in the long run if it leads to better performance and less frequent replacements or repairs.
D. Future-proofing Your Setup
Planning for Future Needs:
Think about how your winching needs might change over time. Investing in a more powerful winch now could save you the hassle and cost of upgrading later.
Scaling Up: If you anticipate needing to pull heavier loads or use the winch more frequently in the future, opting for a 24V winch might be a wise choice even if your current needs are met by a 12V winch.
Versatility and Resale Value: A 24V winch can offer greater versatility for different applications and may also have a higher resale value if you decide to sell it later. Planning ahead ensures that your setup remains effective and reliable as your requirements evolve.
Installation Considerations
A. 12V Winch Installation Basics
12V Winch Installation:
Installing a 12V winch is usually straightforward. Most vehicles are equipped with a 12V electrical system, so the winch can often be connected directly to the existing battery.
Process: The installation typically involves mounting the winch to a suitable location on the vehicle, connecting the power cables to the battery, and running the control cables to a convenient location in the cab.
Ease of Installation: Since the vehicle’s electrical system doesn’t need modifications, the installation is relatively simple and can often be completed with basic tools and mechanical knowledge.
B. 24V Winch Installation Challenges
24V Winch Installation:
Installing a 24V winch can be more complex because most vehicles are not equipped with a 24V electrical system.
Modifications Needed: You may need to install a second battery to create a 24V system, upgrade the alternator, and rewire parts of the vehicle. This can involve significant electrical work and a thorough understanding of the vehicle’s electrical system.
Complexity: Due to these additional requirements, installing a 24V winch often requires more time, effort, and potentially professional assistance to ensure the system is set up correctly and safely.
C. Dual Battery Setups for 24V Systems
Dual Battery Setup:
To achieve a 24V system in a vehicle with a 12V electrical system, a dual battery setup is typically necessary. This involves connecting two 12V batteries in series to create a 24V power source.
Benefits: A dual battery setup provides the necessary voltage for a 24V winch and can also ensure that the vehicle’s starting battery remains isolated and charged, preventing winch use from draining the primary battery.
Considerations: Setting up a dual battery system requires additional components like battery isolators or automatic charging relays to manage the batteries effectively and ensure both batteries are charged properly.
Maintenance and Longevity
A. Battery Care for 12V vs 24V Systems
Battery Maintenance:
- 12V Systems: Regular battery maintenance involves checking the charge level, cleaning terminals, and ensuring the battery is in good condition. Due to the higher current draw, 12V systems might require more frequent maintenance and monitoring.
- 24V Systems: While maintenance practices are similar, 24V systems can offer longer battery life because they draw less current for the same power output. This reduced strain on the batteries can lead to fewer maintenance issues and longer intervals between maintenance checks.
B. Motor and Component Wear Comparison
Wear and Tear:
- 12V Winches: These tend to experience more wear and tear because they draw more current, which generates more heat and places greater stress on the motor and components.
- 24V Winches: These are generally more efficient and generate less heat, leading to reduced wear on the motor and components. This can potentially extend the lifespan of the winch and its parts.
C. Long-term Reliability Factors
Reliability:
- 12V Systems: Regular maintenance is crucial to prevent issues caused by higher heat generation and stress on components. Proper care can ensure long-term reliability.
- 24V Systems: Due to their efficiency and lower heat generation, 24V systems often offer better long-term reliability. The reduced stress on electrical components can lead to fewer breakdowns and longer service life.
FAQ
Can I Convert a 12V Winch to 24V?
While possible, it requires significant electrical modifications and may not be cost-effective.
Do I Need to Upgrade My Alternator for a 24V Winch?
Upgrading the alternator can be necessary to handle the increased electrical load of a 24V system.
Which Winch Voltage is Better for Heavy-duty Use?
24V winches are generally better for heavy-duty use due to their higher power output and efficiency.
Are There Any Safety Differences Between 12V and 24V Winches?
Both systems can be safe if installed and used correctly, but 24V systems may offer better performance in high-demand situations.
How Do 12V and 24V Winches Compare in Terms of Weight?
The weight difference is typically minimal, with other factors like power and performance being more significant considerations.
Conclusion
Choosing between a 12V and 24V winch depends on your vehicle compatibility, winching needs, budget, and long-term plans.
Each system has its advantages and drawbacks, and understanding these can help you make an informed decision.
Explore our top-rated winches with versatile power options to find one that fits your power needs.

